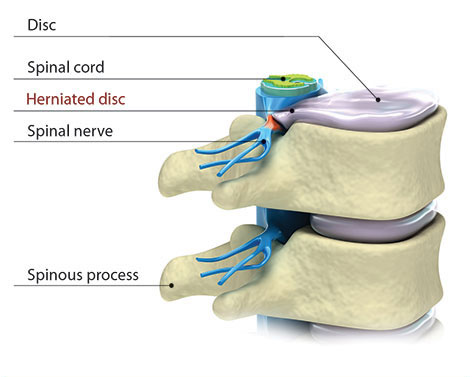
Learn about the shock-absorbing discs that separate the bones in the spine.
Approximately four out of five American adults will experience back pain at some point in their lives. The encouraging news is that most episodes are acute, meaning they resolve on their own within a few days to a week. With conservative measures such as anti-inflammatory medications, physical therapy, or spinal injections, the majority of simple acute back pain improves without the need for surgery.
“Subacute” back pain refers to symptoms lasting between one and four months. When pain persists for four months or longer, it is classified as chronic low back pain. According to the National Institutes of Health, approximately one in five individuals who experience acute low back pain will go on to develop chronic symptoms lasting a year or more.
In some cases, chronic low back pain responds well to treatment. In others, discomfort may continue despite appropriate medical or surgical care. Chronic low back pain is both common and potentially debilitating, affecting an estimated six million adults particularly those age 65 and older. When pain persists beyond six months, individuals often become less active, leading to muscle deconditioning. As muscles and ligaments weaken, they become more vulnerable to strain, creating a cycle in which reduced activity increases the likelihood of further pain and disability.
The growing impact of low back pain is reflected in national health data. In 1990, low back pain ranked sixth among the most burdensome health conditions in the United States. By 2010, it had risen to third surpassed only by Ischemic heart disease and Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Chronic back pain can be especially challenging to treat when diagnostic tests fail to identify a clear structural cause such as a herniated disc or bone spur. Some experts believe that in certain individuals, pain pathways within the nervous system become sensitized. In these cases, even minor strain can trigger amplified pain signals traveling from the spinal cord to the brain.
In other situations, a herniated disc or vertebral issue may be successfully treated, yet pain continues. Researchers suggest that even after healing occurs and imaging appears normal, sensitized nerve pathways may continue to transmit pain signals. These signals can feel just as intense as the original injury. Some experts compare this phenomenon to an image “burned in” on a television or computer screen where the signal persists even though the original source has resolved.
While medications can offer temporary relief for chronic low back pain, long-term reliance on certain drugs may lead to significant side effects and potential harm to internal organs.
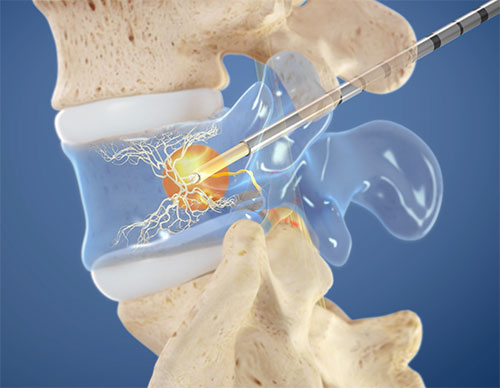
At Texas Spine and Scoliosis, a variety of non-surgical treatment options are available for chronic low back pain. These include structured spine therapy programs, targeted spinal injections, and advanced procedures such as the Intracept® procedure, all designed to reduce pain and restore function without unnecessary surgery.
For more information about the Intracept nonsurgical procedure, click here.
[Top]